
Introduction
Bangladesh has emerged as a significant player in the global garment industry, securing its position as the second-largest garment exporter worldwide. The country’s remarkable journey from economic struggles to becoming a key player in the textile and apparel sector is a testament to its resilience and adaptability.
The roots of Bangladesh’s garment industry can be traced back to the 1970s, a period when the country was grappling with the aftermath of its Liberation War and the challenges of establishing a stable economy. In the early stages, the industry was primarily focused on meeting domestic demand, with limited international exposure. However, a series of economic reforms and strategic decisions paved the way for Bangladesh to enter the global market.
Historical Background The Garment Sector in Bangladesh
The journey of Bangladesh’s garment sector began in the late 1970s. At that time, the country was still struggling with poverty and unemployment after its independence in 1971. A breakthrough came when a few entrepreneurs started small-scale garment factories with the support of foreign investors and technical expertise.
- 1978: The first export-oriented garment factory was established.
- 1980s: The industry saw rapid growth, mainly due to the Multi-Fiber Agreement (MFA), which allowed duty-free access to Western markets.
- 1990s: Bangladesh gradually became a trusted sourcing destination for global buyers.
Today, more than 4,000 garment factories operate in the country, producing billions of dollars’ worth of clothing for international markets.
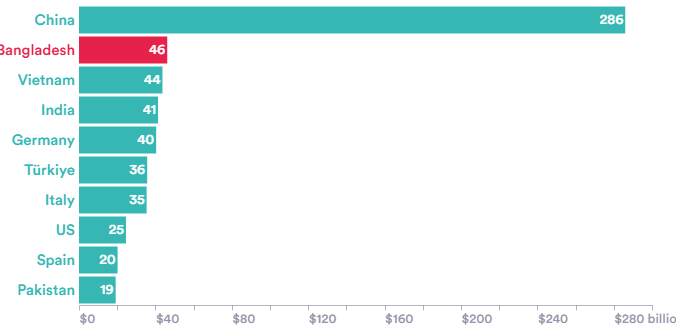
Top ten textile manufacturing countries by export value, 2024
Top 10 Garments Factory in Bangladesh
Importance of the Garment Sector to Bangladesh’s Economy
The garment industry is often described as the backbone of Bangladesh’s economy. Its contributions are immense and multifaceted:
1. Contribution to GDP
The garment sector contributes nearly 12–13% of Bangladesh’s total GDP, making it one of the most significant drivers of economic progress.
2. Export Earnings
Around 84% of Bangladesh’s total export earnings come from the readymade garment (RMG) industry. In the fiscal year 2023–24, garment exports crossed $47 billion, strengthening the country’s position in the global textile market.
3. Employment Generation
The industry employs around 4.5 million workers, with women making up nearly 60–65% of the total workforce. This has played a crucial role in women’s empowerment and social transformation in rural and urban Bangladesh.
4. Poverty Reduction
The garment sector has helped lift millions of families out of poverty by providing jobs and steady income. It has also created opportunities for small businesses, from transport to food supply, indirectly supporting millions more.
Structure of the Garment Industry
The garment industry in Bangladesh is divided into several segments, each playing a vital role in the supply chain.
- Knitwear – T-shirts, sweaters, underwear, and casual wear.
- Woven garments – Shirts, trousers, jackets, and suits.
- Home textiles – Bedsheets, curtains, and pillow covers.
- Specialized garments – Sportswear, denim, workwear, and outerwear.
Knitwear and woven garments together account for the majority of export earnings. Knitwear has grown faster in recent years due to shorter lead times and flexibility in production.
Key Strengths of Bangladesh’s Garment Sector
The industry’s global success can be attributed to several strengths:
- Low Labor Costs
Bangladesh offers one of the most competitive labor costs in the world, making it an attractive sourcing destination for buyers. - Skilled Workforce
Over the years, workers have gained experience and skill in mass garment production, ensuring both efficiency and quality. - Strong Backward Linkage Industry
The development of spinning, dyeing, knitting, and weaving industries has strengthened local supply chains, especially in knitwear. - Government Support
Tax incentives, export-friendly policies, and bonded warehouse facilities have encouraged the growth of the RMG industry. - Geographical Advantage
Bangladesh’s location near major shipping routes in Asia gives it an edge in delivering products to global markets.
Limitations of garment sector of Bangladesh
One of the essential obstacles of this have a look at is its small pattern size that is best 10 samples while the whole populace is 4560 BGMEA registered garment factories in Bangladesh. (Source: BGMEA) This isn’t always enough to show the overall situation of appropriate sustainable production and development in RMG industry of Bangladesh. Additionally, samples are taken only from those organizations which have at least one global certificate on appropriate manufacturing or related issues that confined this thesis paper to discover applicable facts about suitable manufacturing practices in RMG enterprise.
Additionally, data are amassed inside a brief time frame and interview is taken from the ones companies which situated in Dhaka, Savar and Gazipur that constrained the scope of this thesis. This has a look at entirely works in RMG enterprise but sustainable manufacturing exercise is vital for any industry. This observation could be extended to discover the connection of sustainable production exercise and performance in addition to financial impact inside the industry. Further could be prolonged to comparative evaluation between corporations or industries. But this study is done to find out and uphold the possibilities of achieving sustainability or sustainable development in whole RMG sector of Bangladesh.
This has a look at has been carried out at a very initial level. But appropriate manufacturing and sustainable development are a crucial a part of doing surroundings pleasant commercial enterprise. The government, subsidized with the aid of greater studies on this subject be counted, wishes to come forward to encourage and educate the RMG industry to undertake extra sophisticated appropriate.
Role of Women in the Garment Industry

One of the most remarkable aspects of the garment industry is its contribution to women’s empowerment. Millions of women from rural areas have migrated to cities like Dhaka, Gazipur, and Chittagong to work in garment factories.
- Women now make up the majority of the workforce.
- Employment in garments has given women greater financial independence.
- Women workers have gained decision-making power in their families and communities.
This transformation has reshaped the social fabric of Bangladesh, giving women a stronger voice in society.
Challenges Facing the Garment Industry
Despite its impressive growth, the garment sector faces multiple challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable development.
Global buyers demand strict compliance with labor laws, safety standards, and environmental practices. Meeting these requirements can be costly for small and medium-sized factories.
- Low Wages & Worker Welfare: Despite some improvements, wages remain very low, far below the estimated living wage, and worker protests over conditions persist.
- Economic Vulnerability: The sector’s heavy reliance on a single industry makes the economy vulnerable to external shocks.
- International Competition: Loss of duty-free access to the EU in 2026 poses a significant threat, as competitors like Vietnam gain an advantage.
- Sustainability & Compliance: While progress is being made, meeting the growing global demand for sustainability and ethical practices remains an ongoing challenge.
- Infrastructure & Raw Materials: Inadequate infrastructure and a lack of local raw material production contribute to production difficulties and rising costs.
Environmental Concerns

The garment industry, particularly the dyeing and washing processes, has been criticized for polluting rivers and harming the environment. Sustainable practices such as eco-friendly dyes, water recycling, and green factories are gaining importance.
Bangladesh is now home to some of the highest number of green garment factories certified by LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) in the world, showing progress toward sustainability.
Major Export Markets

Bangladesh exports garments to more than 150 countries worldwide.
- European Union (EU) – The largest market, accounting for nearly 50% of exports.
- United States – The second-largest market.
- Canada, Japan, Australia, and the Middle East – Emerging destinations.
Popular international brands like H&M, Zara, Uniqlo, Walmart, Gap, and Primark source a significant share of their clothing from Bangladesh.
Government and Policy Support
The Bangladeshi government has played a crucial role in supporting the garment sector through:
- Export Processing Zones (EPZs).
- Duty-free import of raw materials.
- Back-to-back letters of credit.
- Subsidies on utilities.
- Favorable trade agreements with the EU under GSP (Generalized System of Preferences).
Future Opportunities for the Garment Sector of Bangladesh
The future of Bangladesh’s garment sector looks promising, provided it adapts to changing global demands.
- Automation and AI: Integrating Industry 4.0 technologies like automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
- Modernized Production: A fully modernized ready-made garment sector can attract foreign direct investment and technology transfers.
- Green Manufacturing: With growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, the sector can focus on zero-emission, zero-waste, and energy-efficient processes.
- Worker Welfare: Investing in and improving the welfare of workers, who are essential partners in the industry’s success, is critical for long-term growth and ethical practices.
- Moving Beyond Basic Production: The goal is to evolve beyond basic, low-cost production and diversify product offerings to become a more value-added global hub.
- Upstream Linkages: Developing upstream industries, such as spinning, weaving, and dyeing, can reduce reliance on imports and create a more integrated value chain.
- Skilled Workforce:
Building a skilled workforce and investing in education and training programs is crucial for adapting to global trends and fostering innovation. - Strengthening Trade Relationships: Building stronger international trade relationships and advocating for policy measures that support sustainable and ethical fashion practices are vital.
- Brand Building: The industry needs to move from competing among themselves to building strong brands and gaining global recognition for its good practices.
Social and Cultural Impact of Garment Sector of Bangladesh
Beyond economics, the garment sector has brought profound social changes to Bangladesh:
- Urbanization: Millions have migrated to urban areas for jobs.
- Education: Families with garment workers can afford to send children to school.
- Gender Equality: Women have gained greater social respect and financial security.
- Health Awareness: Access to better healthcare through factory programs.
- Poverty Reduction:
By providing jobs to millions, especially rural migrants, the garment sector has helped families escape poverty and improved overall living standards.
Case Studies of Success
- Green Factories:
Bangladesh is a global leader with many Platinum-rated garment factories and a high concentration of LEED-certified facilities worldwide, a testament to its progress in sustainability. - Digitalization: Some forward-looking factories have adopted automation and ERP systems to manage large-scale orders efficiently.
- Worker Welfare Programs: Factories working with top brands have introduced daycare centers, medical facilities, and housing support for workers.
Conclusion
The garment sector in Bangladesh is not just an industry—it is a lifeline for the nation. It has fueled economic growth, created millions of jobs, empowered women, and transformed society. Despite challenges such as worker rights, global competition, and environmental concerns, the industry continues to thrive and evolve.
With sustainable practices, technological advancements, and strong government support, Bangladesh is well-positioned to strengthen its position as a global leader in apparel manufacturing. The future of the garment industry lies in its ability to adapt, innovate, and meet the rising expectations of international buyers while ensuring the welfare of its workers and the protection of the environment.
The garment sector of Bangladesh truly stands as a symbol of resilience, ambition, and progress on the world stage.




















1 thought on “The Garment Sector in Bangladesh: Growth, Challenges, and Global Impact”